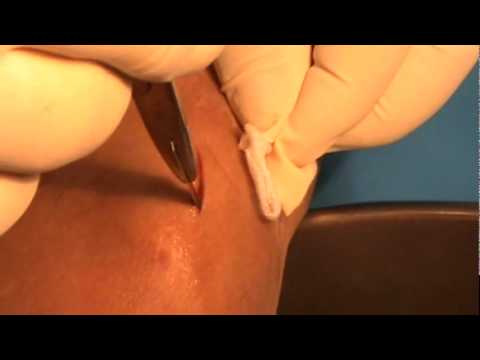
Drenaje de hematoma en pierna - haematoma in leg: drainage
Enviado por CONSULTORIO MÉDICO JAVIER FLORES BUISSON MÁNCORA- PERÚ...
URL: ...
Un hematoma es una acumulación de sangre, causado por la rotura de vasos capilares, que aparece generalmente como respuesta corporal resultante de un golpe, una contusión o una magulladura. También es conocido popularmente como cardenal, moratón, moretón o moradura. Un hematoma adquiere en la zona afectada un color azulado o violáceo al cabo de unos diez minutos, y desaparece de forma natural.
Hematoma en el codo, nueve días después de una extracción de sangre.Los hematomas son equimosis (manchas de la piel), pero también se pueden desarrollar en los órganos internos. Los hematomas pueden migrar gradualmente a medida que las células y los pigmentos efluidos se mueven en el tejido conectivo. Por ejemplo, un hematoma en la base del pulgar se movería lentamente hasta cubrir todo el dedo en una semana.
A hematoma, or haematoma, is an extravasation of blood outside the blood vessels, generally the result of hemorrhage. A hematoma is a pocket or localized collection of blood usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise. Internal bleeding is generally considered to be a spreading of blood within the abdomen or skull, not within muscle.
It is not to be confused with hemangioma which is an abnormal build up of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs.
Hematoma—from Greek αίμα, haima, blood + τωμα, t-oma—indicating a tumor or swelling .
Hematomas can occur within a muscle. Some hematomas form into hard masses under the surface of the skin. This is caused by the limitation of the blood to a subcutaneous or intramuscular tissue space isolated by fascial planes. This is a key anatomical feature that prevents such injuries from causing massive blood loss. In most cases the sac of blood or hematoma eventually dissolves; however, in some cases they may continue to grow or show no change. If the sac of blood does not disappear, then it may need to be surgically removed. Hematomas occur when heparin is given via an intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneously.
The slow process of reabsorption of an hematomas can allow the broken down blood cells and hemoglobin pigment to move in the connective tissue. For example, a patient who injures the base of his thumb might cause a hematoma, which will slowly move all through the finger within a week. Gravity is the main determinant of this process.
Hematomas on articulations can reduce mobility of a member and present roughly the same symptoms as a fracture.